In the world of operating systems, efficient CPU scheduling plays a crucial role in determining how processes are managed and executed. Among several scheduling techniques, Priority Scheduling is widely used due to its ability to assign importance levels to different processes. This page is dedicated to Non-Preemptive Priority Scheduling, and includes 18 carefully selected and solved questions, including previous year questions, to help you fully understand the concept.
Before diving into the questions, let’s briefly understand what preemptive and non-preemptive scheduling mean, and how priority-based scheduling fits into the picture.
Jump To QuestionAnswer : Preemptive Scheduling means that the operating system can interrupt a currently running process if a higher priority process arrives into ready queue. It ensures faster execution of important tasks but can lead to more context switches and increased overhead.
Non-Preemptive Scheduling, it does not interrupt the running process. Once a process starts execution, it runs untill completion — even if a higher priority process arrives in the queue. This makes it simpler and more predictable but might delay urgent tasks.
The Non Preemptive Priority Scheduling algorithm in operating systems allocates CPU to the processes based on priority. Each process is assigned a priority, and the CPU is assigned to the process with the highest priority. Lower-priority processes wait until higher-priority ones finish, ensuring that essential processes get CPU time as needed.
- Step 1: First of all you decide whether you want to give highest priority to the lower priority number or higher priority to the higher priority number? (for ex: we give highest priority to the lower number) (every process will already be given a priority number in the question)
- Step 2: Compare the priority number of each process of the question , and accordingly we will assign the process to ready .
- Step 3: now we will select the process according to highest priority from ready queue and allocate the CPU to it.
- Step 4: If two processes have the same priority, use an alternate scheduling algorithm (e.g., FCFS ) to decide the order. (or we will assign the process which comes first in the question, to the cpu)
- Step 5: Once the process is completed, move to the next highest-priority process.
- Repeat until all processes in the queue have executed.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Ensures important processes execute first. | Can lead to starvation for lower-priority processes. |
| Can be customized to specific needs. | Complexity increases with more processes. |
| Efficient for real-time systems. | May require additional calculations for priority. |
| Flexible for process priority adjustments. | Risk of priority inversion issues. |
| Less overhead for high-priority tasks. | CPU utilization can be low for non-essential tasks. |
| Reduces wait time for critical processes. | Can lead to unpredictable CPU allocation. |
Priority scheduling is often favored in systems that require high responsiveness for critical tasks, such as real-time systems, because it ensures essential processes are given priority access to the CPU. Compared to algorithms like FCFS or Round Robin, priority scheduling minimizes the wait time for critical applications and can be optimized further with priority adjustments, making it adaptable and highly effective for time-sensitive applications.
Question 1 : find the average Turn Around Time and Waiting Time of following processes using Non-Preemptive priority scheduling process scheduling algorithm?
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0 | 8 | 2 |
| P2 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| P3 | 2 | 9 | 3 |
| P4 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
Solution :
lower number represents higher priority (here i take 1 as a highest priority)
Formula:
- Turnaround Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
- Waiting Time = Turnaround Time - Burst Time
- Average Turnaround Time = Sum of Turnaround Times / Number of Processes
- Average Waiting Time = Sum of Waiting Times / Number of Processes
Gantt Chart
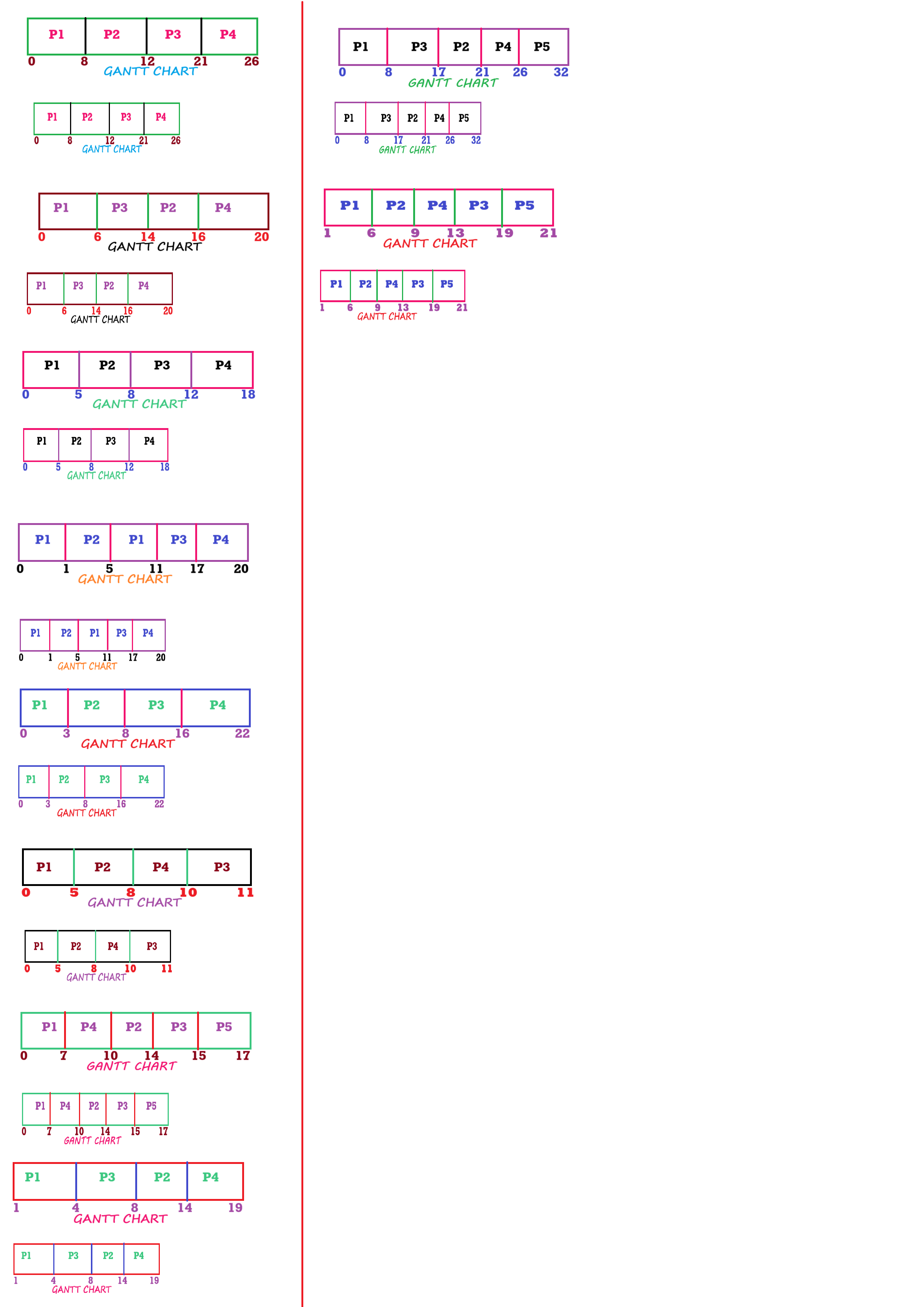
| Process | Completion Time | Turnaround Time | Waiting Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 8 | 8 | 0 |
| P2 | 12 | 11 | 7 |
| P3 | 21 | 19 | 10 |
| P4 | 26 | 23 | 18 |
Average Turnaround Time: (8+11+19+23)/4 = 15.25
Average Waiting Time: (0+7+10+18)/4 = 8.75
Question 2: Given a list of processes with their respective Arrival Times, Burst Times, and Priorities in the table, use the Non-Preemptive Priority Scheduling algorithm to determine the Completion Time, Turnaround Time, and Waiting Time for each process.
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0 | 5 | 2 |
| P2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| P3 | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| P4 | 6 | 2 | 3 |
Solution :
lower number represents higher priority (here i take 1 as a highest priority)
Formula:
- Turnaround Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
- Waiting Time = Turnaround Time - Burst Time
- Average Turnaround Time = Sum of Turnaround Times / Number of Processes
- Average Waiting Time = Sum of Waiting Times / Number of Processes
Gantt Chart
| Process | Completion Time | Turnaround Time (TAT) | Waiting Time (WT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 5 | 5 - 0 = 5 | 5 - 5 = 0 |
| P2 | 8 | 8 - 2 = 6 | 6 - 3 = 3 |
| P3 | 11 | 11 - 4 = 7 | 7 - 1 = 6 |
| P4 | 10 | 10 - 6 = 4 | 4 - 2 = 2 |
Average Turnaround Time:
(5 + 6 + 7 + 4) / 4 = 5.5 units
Average Waiting Time:
(0 + 3 + 6 + 2) / 4 = 2.75 units
Question 3: Calculate the average Turnaround Time, Completion Time, and Waiting Time for the processes listed in the table using the Non-Preemptive Priority Scheduling algorithm.
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| P2 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| P3 | 3 | 6 | 4 |
| P4 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| P5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| P6 | 6 | 1 | 6 |
Solution :
lower number represents higher priority (here i take 1 as a highest priority)
Formula:
- Turnaround Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
- Waiting Time = Turnaround Time - Burst Time
- Average Turnaround Time = Sum of Turnaround Times / Number of Processes
- Average Waiting Time = Sum of Waiting Times / Number of Processes
Gantt Chart
| P1 (1-4) | P2 (4-8) | P3 (8-14) | P4 (14-16) | P5 (16-21) | P6 (21-22) |
| Process | Completion Time | Turnaround Time (TAT) | Waiting Time (WT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 4 | 4 - 1 = 3 | 3 - 3 = 0 |
| P2 | 8 | 8 - 2 = 6 | 6 - 4 = 2 |
| P3 | 14 | 14 - 3 = 11 | 11 - 6 = 5 |
| P4 | 16 | 16 - 4 = 12 | 12 - 2 = 10 |
| P5 | 21 | 21 - 5 = 16 | 16 - 5 = 11 |
| P6 | 22 | 22 - 6 = 16 | 16 - 1 = 15 |
Average Turnaround Time :
(3 + 6 + 11 + 12 + 16 + 16) / 6 = 10.67 units
Average Waiting Time:
(0 + 2 + 5 + 10 + 11 + 15) / 6 = 7.17 units
Gantt Chart
| P1 (1-4) | P2 (4-8) | P3 (8-14) | P4 (14-16) | P5 (16-21) | P6 (21-22) |
Question 4 : Apply the Non-Preemptive Priority Scheduling method to the processes in the table and compute the average Waiting Time, Completion Time, and Turnaround Time.
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| P2 | 2 | 5 | 1 |
| P3 | 4 | 8 | 3 |
| P4 | 6 | 6 | 4 |
Solution :
Formula:
- Turnaround Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
- Waiting Time = Turnaround Time - Burst Time
- Average Turnaround Time = Sum of Turnaround Times / Number of Processes
- Average Waiting Time = Sum of Waiting Times / Number of Processes
Gantt Chart
| Process | Completion Time | Turnaround Time | Waiting Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| P2 | 8 | 6 | 1 |
| P3 | 16 | 12 | 4 |
| P4 | 22 | 16 | 10 |
Average Turnaround Time: (3+6+12+16)/4 = 9.25
Average Waiting Time: (0+1+4+10)/4 = 3.75
Question 5 :Calculate the average Turnaround Time, Completion Time, and Waiting Time for the given set of processes using the Non-Preemptive Priority Scheduling algorithm. The Arrival Time, Burst Time, and Priority of each process are provided in the table.
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0 | 5 | 3 |
| P2 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| P3 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| P4 | 3 | 6 | 4 |
Solution :
lower number represents higher priority (here i take 1 as a highest priority)
Formula:
- Turnaround Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
- Waiting Time = Turnaround Time - Burst Time
- Average Turnaround Time = Sum of Turnaround Times / Number of Processes
- Average Waiting Time = Sum of Waiting Times / Number of Processes
Gantt Chart
| Process | Completion Time | Turnaround Time | Waiting Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| P2 | 8 | 7 | 4 |
| P3 | 12 | 10 | 6 |
| P4 | 18 | 15 | 9 |
Average Turnaround Time: (5+7+10+15)/4 = 9.25
Average Waiting Time: (0+4+6+9)/4 = 4.75
Question 6: Non-Preemptive Priority Scheduling
find the average Turn Around Time and Waiting Time of following processes using Non-Preemptive priority scheduling process scheduling algorithm? Consider the following processes with their Arrival Time, Burst Time, and Priority which is given in the table.
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| P2 | 2 | 6 | 2 |
| P3 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| P4 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
Solution :
lower number represents higher priority (here i take 1 as a highest priority)
Formula:
- Turnaround Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
- Waiting Time = Turnaround Time - Burst Time
- Average Turnaround Time = Sum of Turnaround Times / Number of Processes
- Average Waiting Time = Sum of Waiting Times / Number of Processes
Gantt Chart
| Process | Completion Time | Turnaround Time (TAT) | Waiting Time (WT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 4 | 4 - 1 = 3 | 3 - 3 = 0 |
| P2 | 14 | 14 - 2 = 12 | 12 - 6 = 6 |
| P3 | 8 | 8 - 3 = 5 | 5 - 4 = 1 |
| P4 | 19 | 19 - 5 = 14 | 14 - 5 = 9 |
Average Turnaround Time:
(3 + 12 + 5 + 14) / 4 = 8.5 units
Average Waiting Time:
(0 + 6 + 1 + 9) / 4 = 4 units
Question 7: A set of processes is given with Arrival Time, Burst Time, and Priority values in the table. Use the Non-Preemptive Priority Scheduling algorithm to calculate each process's Completion Time, Turnaround Time, and Waiting Time.
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
| P2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| P3 | 3 | 6 | 4 |
| P4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| P5 | 5 | 2 | 5 |
Solution :
lower number represents higher priority (here i take 1 as a highest priority)
Formula:
- Turnaround Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time
- Waiting Time = Turnaround Time - Burst Time
- Average Turnaround Time = Sum of Turnaround Times / Number of Processes
- Average Waiting Time = Sum of Waiting Times / Number of Processes
Gantt Chart
| Process | Completion Time | Turnaround Time (TAT) | Waiting Time (WT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 6 | 6 - 1 = 5 | 5 - 5 = 0 |
| P2 | 9 | 9 - 2 = 7 | 7 - 3 = 4 |
| P3 | 19 | 19 - 3 = 16 | 16 - 6 = 10 |
| P4 | 13 | 13 - 4 = 9 | 19 - 4 = 5 |
| P5 | 21 | 21 - 5 = 16 | 16 - 2 = 14 |
Average Turnaround Time:
(5 + 7 + 16 + 9 + 16) / 5 = 10.6 units
Average Waiting Time:
(0 + 4 + 10 + 5+ 14) / 5 = 6.6 units
