Here are 11 questions on Buddy System. Each question is presented in a table format. each question is solved in explained form.
What is Buddy System in Operating System ?
The Buddy System is a technique for memory allocation and management utilized in operating systems. It works by dividing memory into partitions to meet allocation requests while aiming to reduce fragmentation. In this approach, memory is divided into blocks that are sized in powers of 2.
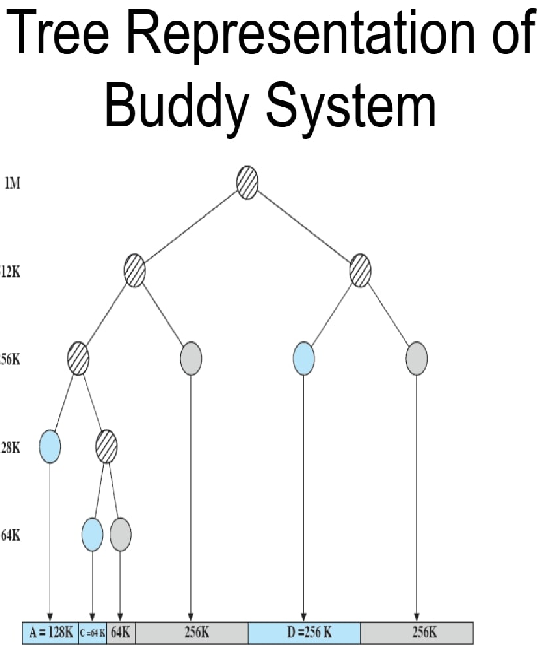
Method to Solve Buddy System Questions
- Step 1: Determine the size of the memory block needed for allocation.
- Step 2: Identify the smallest power of 2 that can fit the required memory size.
- Step 3: Iteratively divide the available memory block into smaller blocks (buddies) until you reach the desired block size.
- Step 4: Allocate the memory block to the process that requested it.
- Step 5: When the process releases the memory, combine it with its buddy if that buddy is free, creating a larger block.
- Step 6: Continue this process for any future allocation or deallocation requests.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Buddy System
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Minimizes internal fragmentation by using power-of-2 blocks. | Leads to external fragmentation if block merging is not possible. |
| Efficient block splitting and merging process. | Requires complex implementation logic. |
| Supports dynamic memory allocation and deallocation. | Limits memory allocation to power-of-2 sizes, potentially wasting memory. |
| Can handle multiple allocation requests concurrently. | Merging and splitting may lead to performance overhead. |
| Enables coalescing of adjacent free blocks for better memory utilization. | May cause fragmentation for varying allocation sizes. |
| Easy to track memory usage using buddy indexing. | Wastes memory when small allocations do not fit well in large blocks. |
Why Buddy System is Better Than Other Algorithms
The Buddy System is often preferred over other memory allocation algorithms (like First Fit, Best Fit, Next Fit and Worst Fit) due to its efficient block splitting and merging mechanism, which minimizes internal fragmentation and allows for quick allocation and deallocation. Its use of power-of-2 block sizes simplifies memory management and reduces the complexity of maintaining free memory lists. However, it still requires careful management to handle external fragmentation effectively.
Question 1 : Suppose the OS on your computer uses the buddy system for memory management. Initially, the system has 1 megabyte (1024K) block of memory available, which begins at address zero. Show the results of each request/release via successive figures.
| A :Request 28K |
| B :Request 232K |
| C :Request 60K |
| D :Request 100K |
| E :Request 30K |
| Release A |
| Release C |
| F : Request 20K |
| G : Request 48K |
After memory is allocated to process F, how much internal Fragmentation exists in the system?
Solution :
| 1024K |
| 512K | 512K |
| 128K | 128K | 256K | 512K |
| 64K | 64K | 128K | 256K | 512K |
| 32K | 32K | 64K | 128K | 256K | 512K |
| A = 32K | 32K | 64K | 128K | 256K | 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 4K
B : request 232K
| A = 32K | 32K | 64K | 128K | B = 256K | 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 24K
C : request 60K
| A = 32K | 32K | C = 64K | 128K | B = 256K | 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 4K
D : request 100K
| A = 32K | 32K | C = 64K | D = 128K | B = 256K | 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 28K
E : request 30K
| A = 32K | E = 32K | C = 64K | D = 128K | B = 256K | 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 2K
Release A
| 32K | E = 32K | C = 64K | D = 128K | B = 256K | 512K |
Release C
| 32K | E = 32K | 64K | D = 128K | B = 256K | 512K |
F : request 20K
| F = 32K | E = 32K | 64K | D = 128K | B = 256K | 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 12K
G : request 48K
| F = 32K | E = 32K | G = 64K | D = 128K | B = 256K | 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 16K
Question 2 : Suppose the OS on your computer uses the buddy system for memory management. Initially, the system has 1 megabyte (1024K) block of memory available, which begins at address zero. Show the results of each request/release via successive figures.
| A :Request 100K |
| B :Request 400K |
| C :Request 40K |
| D :Request 60K |
| E :Request 30K |
| F :Request 20K |
| G :Request 42K |
| Release A |
| Release C |
| G : Request 20K |
| Release B |
After memory is allocated to process G, how much internal Fragmentation exists in the system?
solution :
| 1024K |
| 512K | 512K |
| 128K | 128K | 256K | 512K |
| A = 128K | 128K | 256K | 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 28K
B : request 400K
| A = 128K | 128K | 256K | B = 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 112K
C : request 40K
| A = 128K | 128K | 256K | B = 512K |
| A = 128K | C = 64K | 64K | 256K | B = 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 24K
D : Request 60K
| A = 128K | C = 64K | D = 64K | 256K | B = 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 4K
E : Request 30K
| A = 128K | C = 64K | D = 64K | 128K | 128K | B = 512K |
| A = 128K | C = 64K | D = 64K | 64K | 64K | 128K | B = 512K |
| A = 128K | C = 64K | D = 64K | E = 32K | 32K | 64K | 128K | B = 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 2K
F : request 20K
| A = 128K | C = 64K | D = 64K | E = 32K | F = 32K | 64K | 128K | B = 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 12K
G : request 42K
| A = 128K | C = 64K | D = 64K | E = 32K | F = 32K | G = 64K | 128K | B = 512K |
Internal Fragmentation = 22K
Release A
| 128K | C = 64K | D = 64K | E = 32K | F = 32K | G = 64K | 128K | B = 512K |
Release C
| 128K | 64K | D = 64K | E = 32K | F = 32K | G = 64K | 128K | B = 512K |
G : request 20K
| 128K | G = 32K | 32K | D = 64K | E = 32K | F = 32K | G = 64K | 128K | B = 512K |
Internal Fragmentation : 12K
Release B
| 128K | G = 32K | 32K | D = 64K | E = 32K | F = 32K | G = 64K | 128K | 512K |
Question 3 : Suppose the OS on your computer uses the buddy system for memory management. Initially, the system has 1 megabyte (1024K) block of memory available, which begins at address zero. Show the results of each request/release via successive figures.
| A :Request 62K |
| B :Request 112K |
| C :Request 52K |
| D :Request 60K |
| E :Request 245K |
| F :Request 64K |
| Release A |
| Release B |
| G : Request 40K |
After memory is allocated to process G, how much internal Fragmentation exists in the system?
solution :

previous year question